Cybercriminals are always trying to find their way in.
Gone are the days of cyber security not being at the forefront of your risk management when it comes to protecting your business (and even your home). It is no longer a matter of if but when.
With cybercriminals always on the hunt for a way in, their persistence should be matched with your army of not only security in place to try to prevent a breach, but cyber insurance for when those cyber castle walls come tumbling down. Cyber Liability Insurance will help clean up the aftermath and provide help through each next step in recovering from an attack.
You don’t need to be an expert, just Be In The Know.
Cybersecurity risks and breaches have been amplified over the past 2 years.
- The number of cyberattacks and data breaches increased by 15.1% from 2020 to 2021.
- Cybercriminals can penetrate 93% of company networks.
- Credential compromise is the main way that cybercriminals get into networks (71%).
A typical data breach costs an average of $2.4 million to investigate and recover from, with 63% of organizations being breached in the past year. Yet even with these staggering costs and increased number of attacks, only 14% of small to medium-sized businesses have coverage limits in excess of $600,000.
The insurance industry has seen a dramatic increase in claims frequency, with a 40% increase in ransomware attacks and 54% increase in fund transfer fraud attacks.
So how can Cyber Liability Insurance help?
Cyber Liability Insurance is critical for businesses to protect themselves and their shared or stored data. A cyberattack or data breach may look like a cybercriminal breaching your IT infrastructure and stealing your customers’ Social Security numbers, credit card numbers, bank account information, and/or health records. Cyber Liability insurance can aid in covering the costs arising from the loss obtained through these devastating data breaches and cybersecurity issues. These costs can include:
- lost income due to a cyber event
- costs associated with notifying affected customers
- costs for recovering compromised data
- costs for repairing damaged computer systems
- lawsuits, and more
As severity and frequency increase, carriers are getting stricter and asking businesses for more when it comes to their cybersecurity preparation. Presenting a business to the carrier who is being proactive in their cyber preparedness and response is always the best strategy.
When you develop healthy cyber habits, there will be better outcomes.
As cyber crimes continue increasing in frequency and severity, leading to an increased demand for cyber coverage, many Cyber Insurance carriers are requiring companies to adhere to a number of security control requirements to lessen their risk exposure before they will insure you.
8 Actionable Steps You Should Take for the Cyber Security of Your Business
If you want protection, here are some actionable steps that you should take to not only prepare for cyberattacks, but to help obtain cyber insurance with the best coverage at the best rate:
1. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all logins. Cybercriminals look for any network vulnerabilities, including any openings not protected by MFA. Passwords alone won’t protect a business’s network, so organizations must require additional forms of authentication to lessen their risk. MFA should be enabled for email, critical system access, and remote access.
2. Create, test, and update an incident response plan. Your company should create an incident response plan outlining how you’ll identify, respond, and recover from a cyberattack or data breach to minimize damages and repercussions.
3. Tighten up on access control. Stolen credentials are the most common way to breach a network, and one way to prevent this is by implementing a strong framework of systems and technologies that allows IT managers to manage electronic or digital identities. This will better control which users have access to critical information and improve online security. It’s also important to limit user access to only the information that’s required for them to do their jobs. Adjust permissions when employees’ roles change, and remove access completely once employees leave the organization.
4. Retire older devices, systems, and software. Cybercriminals often target older systems, such as older versions of Microsoft or old servers, thinking their security in more vulnerable because security patches are no longer being released for these systems.
5. Install advanced endpoint security solutions. Endpoint security is the practice of securing endpoints or entry points of user devices such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices from being exploited by malicious attacks. There should be a security system in place to protect these endpoints on a network or in the cloud by providing comprehensive protection from sophisticated malware.
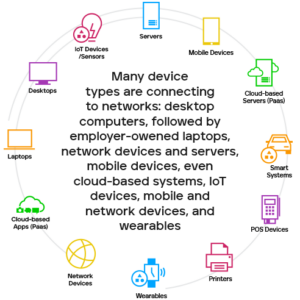
Examples of Endpoint Devices :
- Tablets
- Mobile devices
- Smart watches
- Printers
- Servers
- ATM machines
- Medical devices
If a device is connected to a network, it is considered an endpoint. With the growing popularity of BYOD (bring your own device), the number of individual devices connected to a company’s network can be significantly high.
6. Have backup systems. Your business should review and test their recovery capabilities often. You need offline backup systems in case of ransomware attacks, data corruption, data loss, and other malicious events. Backups should be encrypted and isolated from unsecured networks.
7. Provide security training for employees. All employees should be trained to understand the threat of cybercrimes and the potentially huge ramifications from a cyberattack. Make sure employees understand the importance of strong passwords and know what to do (and not do) in a variety of situations. For instance, they should never open an attachment from an unknown sender, share their passwords, or leave their company computer unattended in a public place. Let employees know the proper protocols for reporting concerns and suspicious cyber behaviors.
8. Create separate IT and cybersecurity roles. Businesses should have separate IT and cybersecurity roles, where the IT teams can focus on keeping the technology running smoothly and the cybersecurity experts can scan for suspicious activity and keep up with the ever-changing cyber threat landscape.
|
|
|